What is MS?
MS or Multiple Sclerosis is a serious neurological disorder in which the central nervous system of the body is impaired in its functioning. MS is one of the most common neurological diseases affecting young adults and according to latest studies, the disease is twice as more common among women as compared to men. 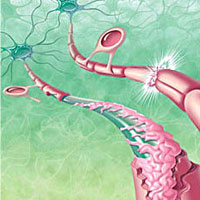
MS and the Central Nervous System
What is Multiple Sclerosis The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system which is made up of the spinal cord, the brain and optic nerves. The spinal cord is responsible for sending sensory information from the peripheral nervous system to the brain, conducting motor information and acting as a reflex center for the body. The brain plays a role in receiving the information sent by the spinal cord via the axons, processing it and coordinating the motor outputs of the body. Together, the functioning of the spinal cord and brain control the efficiency of the body to behave in a certain manner.
The communication between the spinal cord and brain takes place through the cells of the optic nerves which send electrical signals through long filaments or fibers called axons. The axons of nerve cells or neurons carry electrical signals or messages between different locations. These axons are protected by a myelin sheath that is important to the role of the communication by providing chemicals to the nerve cells. The Multiple Sclerosis disease causes the immune system of the body to attack its own myelin sheath leading to ineffective communication between the nerves cells of the brain and spinal cord or no communication at all.
The name Multiple Sclerosis refers to the multiple scars or the lesions that are formed in the white matter of the brain and the spinal cord because of the damaged myelin. MS is also called as an inflammatory disease which means that the immune cells most commonly found in the blood have been displaced from their position towards the brain because of a broken cellular partition between the brain and the blood stream. As the water and blood cells move from the blood stream into the nervous system tissue, swelling occurs in the myelin lesions which impairs the functions of the central nervous system. When the myelin sheath is attacked and damaged, the axons have some ability to compensate for the loss by rearranging signaling molecules but the speed as well as strength of the signals traveling through is affected.
While MS is usually diagnosed in young adults, it is rarely found in children under the age of 12 and adults over the age of 55. While there are no valid theories related to the causes of the disease, researchers are of the opinion that people with a family history of MS or those who live in a region where the incidence of MS is more common are at a relatively higher risk of getting the disease.